Global Response to Climate Change: COP26 Outcomes and Next Steps for Sustainability
Global Response to Climate Change: COP26 Outcomes and Next Steps for Sustainability
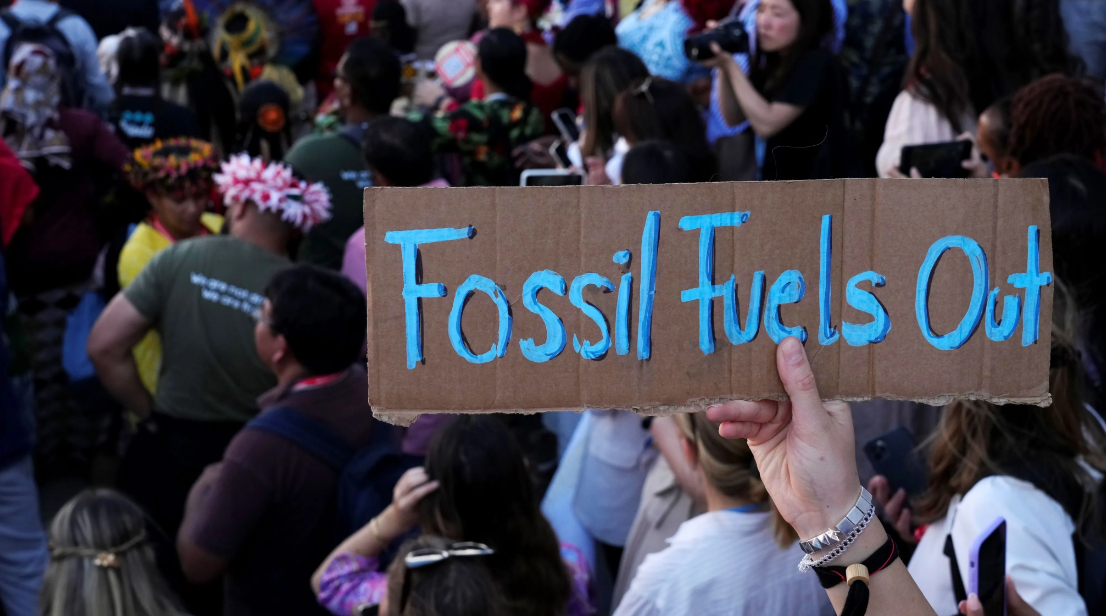
The 26th United Nations Climate Change Conference of the Parties, commonly referred to as COP26, held in Glasgow, Scotland, was a pivotal moment in the global fight against climate change. As the world grapples with the urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change, COP26 served as a platform for nations to come together, negotiate, and commit to concrete actions to address this pressing issue. In this article, we’ll examine the outcomes of COP26, analyze the progress made in the global response to climate change, and explore the next steps for sustainability in the wake of the conference.
Understanding COP26:
COP26, held from October 31 to November 12, 2021, brought together representatives from nearly 200 countries, as well as leaders from government, industry, civil society, and academia. The conference aimed to accelerate action towards the goals of the Paris Agreement, which include limiting global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels and pursuing efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
Key Outcomes of COP26:
- Net-Zero Commitments: Several countries, including major emitters such as the United States, China, and India, announced commitments to achieve net-zero emissions by mid-century or soon after. These pledges are significant steps towards decarbonizing the global economy and achieving long-term climate goals.
- Emissions Reduction Targets: Many countries strengthened their emissions reduction targets under the Paris Agreement, pledging to take more ambitious actions to curb greenhouse gas emissions in the coming years. These enhanced targets are essential for closing the emissions gap and limiting global warming to safe levels.
- Financial Commitments: COP26 saw pledges of financial support from developed countries to assist developing nations in their climate mitigation and adaptation efforts. These commitments include funding for renewable energy projects, climate resilience initiatives, and technology transfer to vulnerable countries.
- Coal Phase-Out: A landmark agreement was reached to phase out unabated coal power and significantly reduce methane emissions. While not all countries signed onto this agreement, it represents a significant step towards transitioning to cleaner energy sources and reducing the carbon footprint of the energy sector.
- Nature-Based Solutions: COP26 emphasized the importance of nature-based solutions, such as reforestation, afforestation, and ecosystem restoration, in addressing climate change. These natural climate solutions can help sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and enhance the resilience of ecosystems to climate impacts.
Challenges and Criticisms:
While COP26 yielded several positive outcomes, it also faced criticism for falling short of expectations in certain areas:
- Ambition Gap: Despite some countries strengthening their emissions reduction targets, overall, the commitments made at COP26 are still insufficient to meet the goals of the Paris Agreement. There remains a significant ambition gap between current pledges and what is needed to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
- Loss and Damage: The issue of loss and damage, referring to the impacts of climate change that are beyond the capacity of vulnerable countries to cope with, received inadequate attention at COP26. Many developing nations called for more substantial financial support and mechanisms to address loss and damage, but concrete commitments in this area were lacking.
- Fossil Fuel Subsidies: Despite calls to end fossil fuel subsidies, there was little progress on this front at COP26. Subsidies for the production and consumption of fossil fuels continue to undermine efforts to transition to clean energy and reduce emissions.
- Equity and Justice: Equity and justice considerations, particularly the principle of common but differentiated responsibilities, were central to discussions at COP26. However, there were disagreements over how to operationalize these principles and allocate responsibilities between developed and developing countries.
Next Steps for Sustainability:
In the aftermath of COP26, it is essential to build on the momentum generated by the conference and take decisive actions to accelerate the transition to a sustainable, low-carbon future. Some key next steps include:
- Implementing and Strengthening Climate Policies: Countries must follow through on their commitments made at COP26 by implementing robust climate policies and regulations to reduce emissions and achieve their targets. This may include enacting carbon pricing mechanisms, incentivizing renewable energy deployment, and phasing out fossil fuel subsidies.
- Investing in Clean Energy and Infrastructure: Governments, businesses, and investors should prioritize investments in clean energy technologies, infrastructure, and innovation. This includes scaling up renewable energy deployment, enhancing energy efficiency, and investing in sustainable transportation and infrastructure projects.
- Enhancing Climate Finance: Developed countries must fulfill their financial commitments to support climate mitigation and adaptation efforts in developing countries. This includes providing additional funding for climate finance mechanisms such as the Green Climate Fund and the Adaptation Fund, as well as supporting technology transfer and capacity-building initiatives.
- Promoting Nature-Based Solutions: Nature-based solutions, such as reforestation, conservation, and sustainable land management, should be integrated into climate action plans. Protecting and restoring natural ecosystems not only helps mitigate climate change but also provides co-benefits for biodiversity conservation, water security, and livelihoods.
- Engaging Stakeholders and Civil Society: Collaboration and engagement with stakeholders, including civil society organizations, businesses, indigenous communities, and youth activists, are essential for driving climate action forward. Governments should involve diverse voices in decision-making processes and ensure transparency, accountability, and inclusivity in climate policy development and implementation.
Conclusion:
COP26 was a critical moment in the global response to climate change, highlighting the urgency of the climate crisis and the need for ambitious, collective action to address it. While the outcomes of the conference represent progress towards the goals of the Paris Agreement, there is still much work to be done to meet the targets and avoid the worst impacts of climate change. Moving forward, it is imperative that countries, businesses, and individuals redouble their efforts to accelerate the transition to a sustainable, low-carbon future and build a more resilient and equitable world for future generations.
For more information visit: cryptcpm.tech
For more information visit: newsburing.com